Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0 TCP/IP
These WinSock tutorials are designed to run on a LAN using
TCP/IP. This means that your machine must have a network card installed
to run these programs. The network card must also be configured for
TCP/IP. Most home computers with a modem have TCP/IP configured for
their dial-up adapter. This is does not mean that the LAN card is
able to use TCP/IP. Usually, the default protocols for a LAN card
are NetBEUI and IPX/SPX. You may have to configure TCP/IP manually
for your LAN card.
How to check if your LAN card is configured to work with TCP/IP:
First, open your Control Panel.
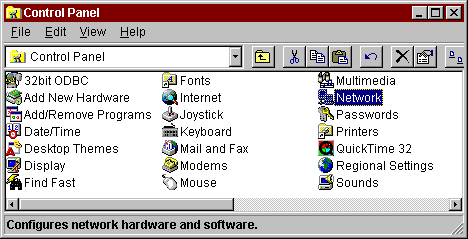
Choose the "Network" icon. This will bring up your Network
dialog.
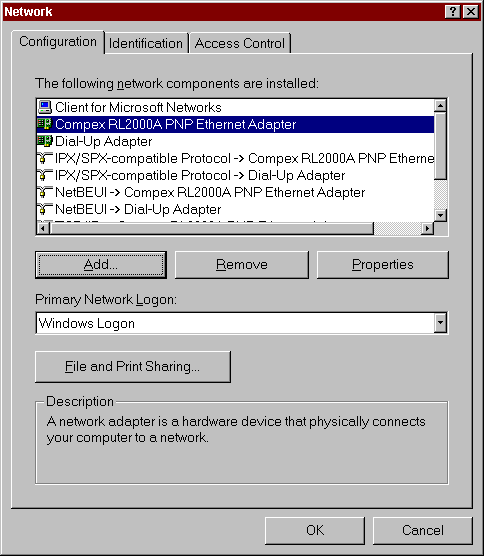
Select your LAN card adapter. (Not your dial-up adapter!) Bring up
the Properties dialog for your adapter.
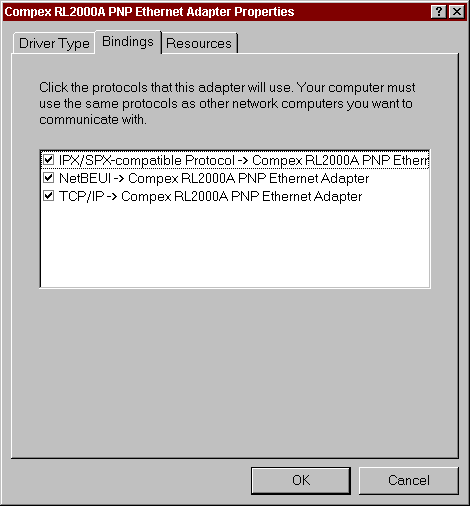
Go to the "Bindings" tab. You should see a check mark in
the TCP/IP box. This tells you that TCP/IP is bound to your network
card.
Additional Settings:
You need to verify the settings of a few more properties before you can
be sure your LAN card is ready to use with TCP/IP. Go back to the
Network dialog and select the TCP/IP entry that is bound to your LAN card.
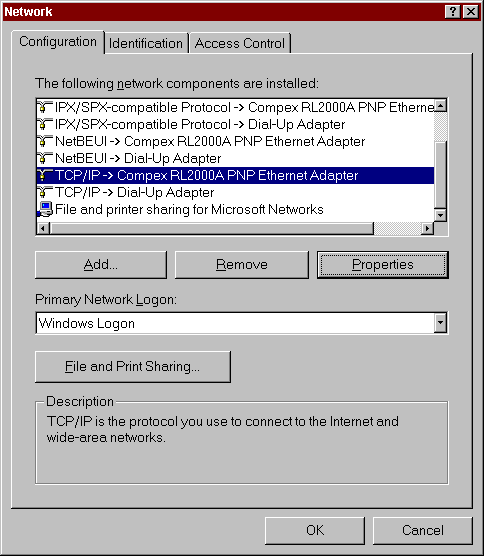
Select the "Properties" button to bring up the TCP/IP configuration
dialog for that adapter.
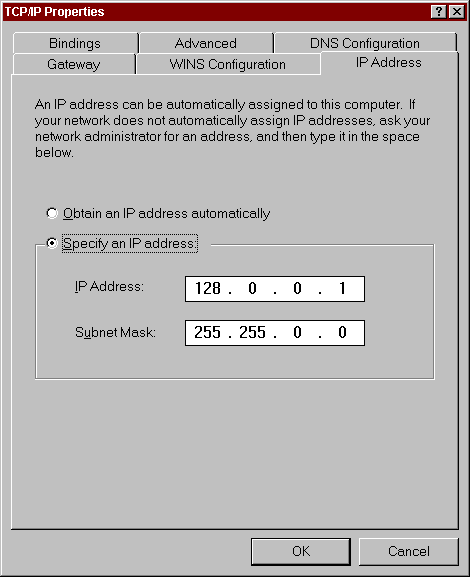
Choose the "IP Address" tab. You must specify a valid IP address.
Please note that these WinSock programs will only be able to communicate
with other WinSock programs that are in the same address class. The
IP address classes are as follows:
Class A: 1.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255
Class B: 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255
Class C: 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255
Class D: 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255
Class E: 240.0.0.0 to 247.255.255.255
If you are in doubt of what address to use, you should probably choose
an address that is in Class B.
Back to Winsock Tutorials Main Page




